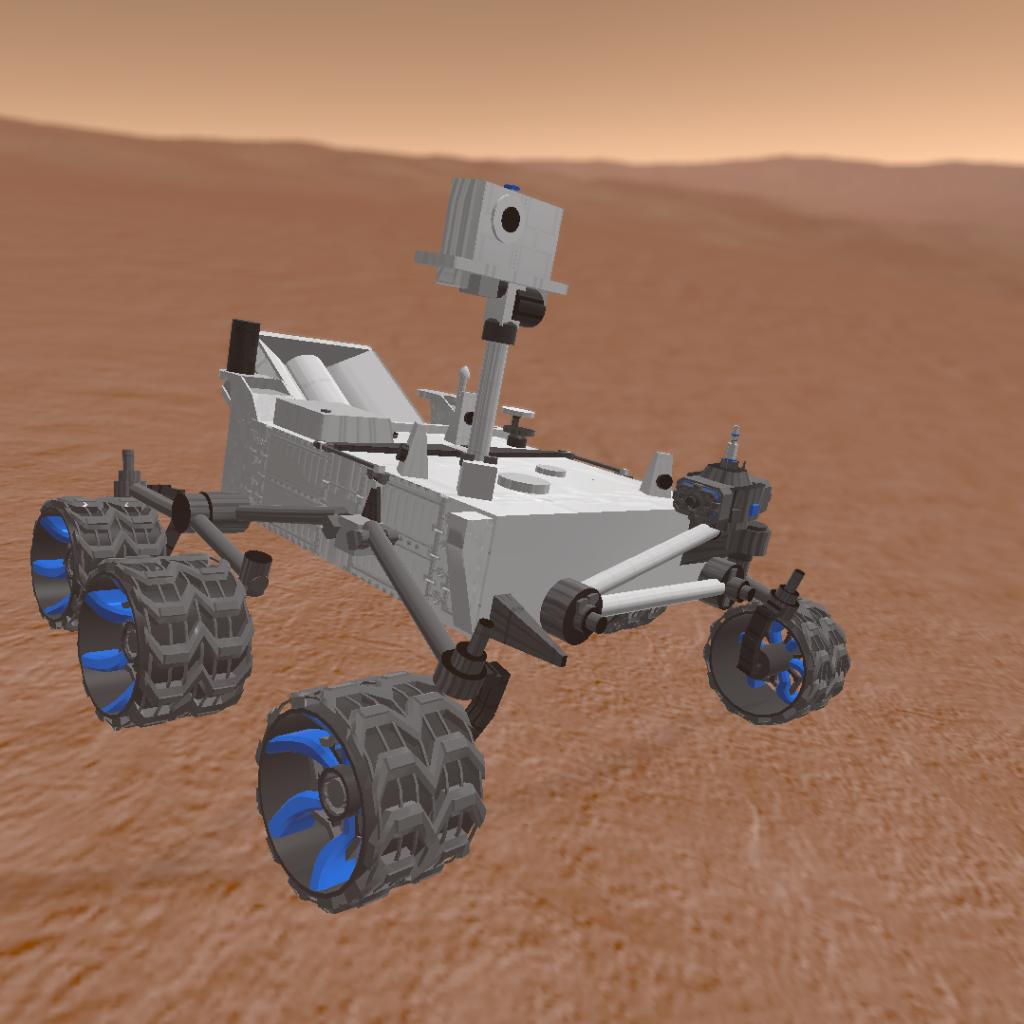
The curiosity rover is a car-sized Mars remote-controlled vehicle. With a total investment of $2.5 billion, it is the most expensive Mars mission ever.
Curiosity blasted off on Nov. 26, 2011, and has been in orbit to Mars ever since. Curiosity landed in a mountain range near the center of gale crater on Mars at 13:31 Beijing time on August 6, 2012.
The rover will spend a Martian year -- about 687 earth days, or almost two years -- on the planet to determine whether there was or is life on Mars.
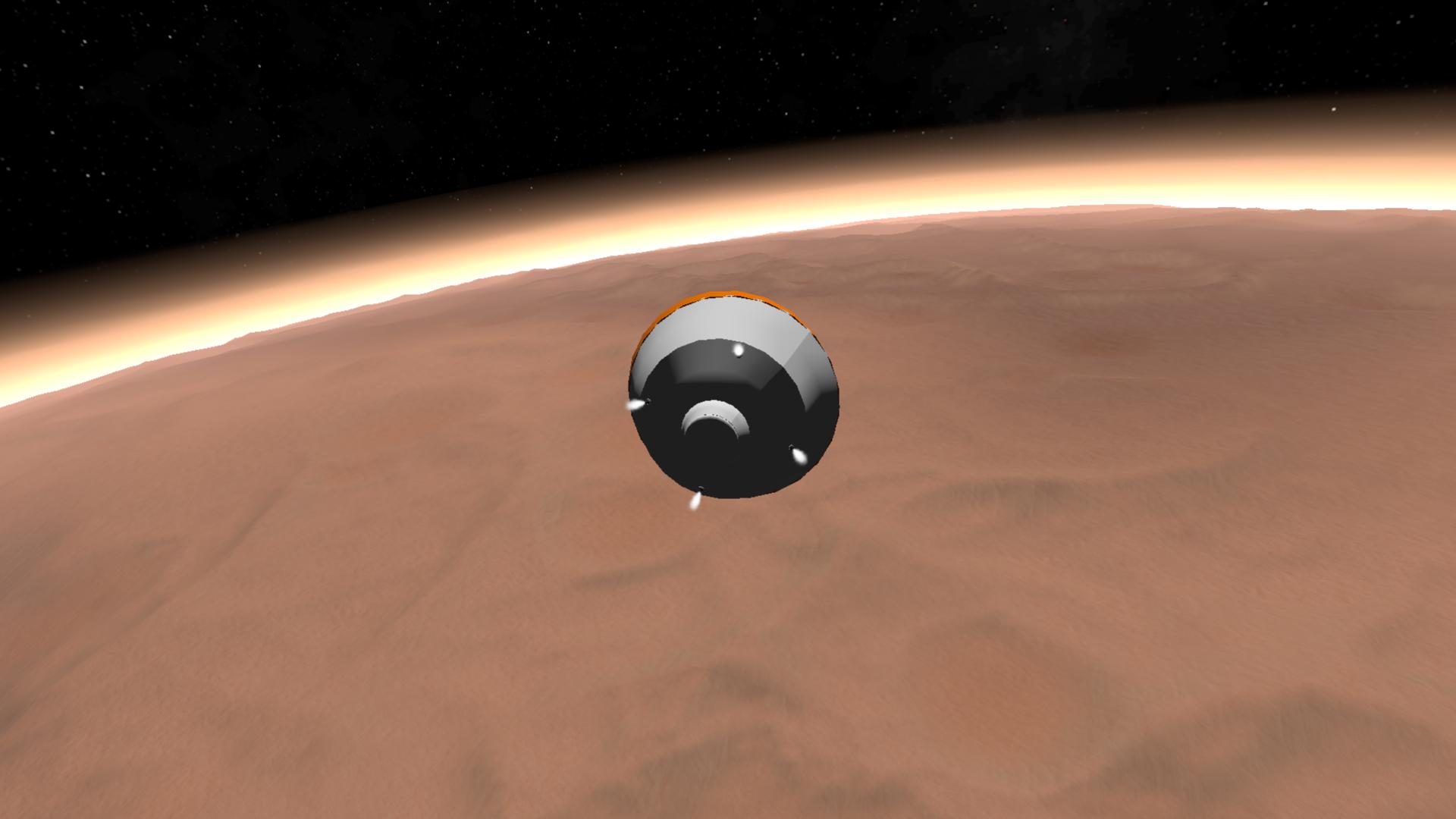
One of the difficulties with landing curiosity was that the lander had to slow down from 21,200 kilometers per hour to zero in six and a half minutes.
When curiosity landed on Mars, the most exciting part was the air lift. The space agency used a new "skycrane" system to bring curiosity to a standstill about 20 meters above the surface of Mars, then lowered it. Because the system had never been physically rehearsed before, it was the biggest mystery of landing.
In 7 minutes, it want to cut by about 20900 kilometers per hour to 0, to complete a series of actions, including the use of a parachute, lit the rockets for landing, and carefully put it in the crater lest produce dust cloud, etc., make the quality of 3 tons, including rover lander down to smooth landing speed from the bullet; It would have to execute hundreds of programs, half a million lines of code, correctly, and if one of them went wrong, curiosity would most likely crash into the Martian surface.
Sophisticated instruments
The curiosity rover is loading the rover
The equipment that curiosity brought to Mars is the most specialized and advanced instrument ever sent to Mars. The curiosity device can lift heavy objects.
The two eyes on its "head" are two cameras, one of which can tell whether a basketball or football is on the other side across seven football fields. The other, when curiosity arrives at a new location, can take 150 photos in 25 minutes and then compose a panoramic image.
Curiosity is also carrying an instrument called a "chemical camera," which can fire lasers that hit rocks or soil up to seven meters away. Material hit by a laser produces plasma, and the camera measures the composition of the object by looking at the spectrum of the plasma. The spectrometer in the device is capable of measuring 6,144 different wavelengths of light, and the light emitted by ionized substances has a specific wavelength. The chemical camera has enough range to help scientists find the next target for close-up sampling and analysis.
Another "alpha particle X-ray spectrometer" can detect as little as 1.5 percent of the rock in a quick 10-minute test. Given three hours, it would be able to detect substances of the order of a millionth. It is particularly sensitive to substances such as sulphur, chlorine and bromine, which are closely related to the production of salt, and may reveal whether they have ever acted with water.
Curiosity has two instruments that directly analyze rock and soil samples, the chemistry and mineralogy analyzer and the Mars sample analysis facility, which rely on curiosity's robotic arm to take samples.
Curiosity also has a powerful tool in its search for water, called the dynamic neutron reversibility device. The device was actually used for oil exploration earlier on earth, emitting neutrons and then determining the presence of hydrogen by observing the energy changes that occur when neutrons interact with hydrogen nuclei. It was later redesigned for lunar and Martian exploration. In 2002, the Mars Odyssey spacecraft used the device to find water ice underground at high latitudes on Mars.
Exploration program
Images of Mars from the curiosity rover are being reloaded
Curiosity's goal this time is to look for carbon-based organisms. Curiosity will cruise the Martian surface, completing an experimental project that will take about two years.
Opportunity and spirit previously entered a small Mars crater and were able to climb a gentle slope, but curiosity will climb mount sharp, about 5,000 meters above gale. By analyzing the surface of mount sharp, curiosity hopes to learn more about the history of Mars.
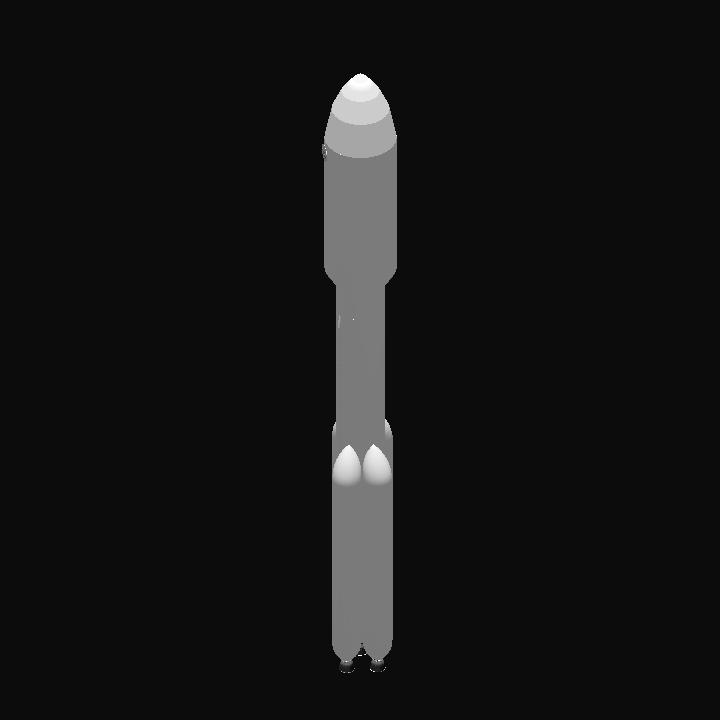
GENERAL INFO
- Successors 2 craft(s)
- Created On: Android
- Game Version: 0.8.402.0
- Price: $58,214k
- Number of Parts: 443
- Dimensions: 99 m x 16 m x 16 m
PERFORMANCE
- Total Delta V: 96.4km/s
- Total Thrust: 14.9MN
- Engines: 11
- Wet Mass: 4.37E+5kg
- Dry Mass: -885,274kg
STAGES
| Stage | Engines | Delta V | Thrust | Burn | Mass |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | 36.1km/s | 13.6MN | 5.0m | 4.37E+5kg |
| 4 | 1 | 37.2km/s | 1.1MN | 25.5m | 90,499kg |
| 9 | 4 | 23.1km/s | 151kN | 9.5m | 11,555kg |
9 Comments
- Log in to leave a comment
-
-
-
-
-
4,910 SouthNoel6.0 years ago
@Lolwhydoiexist Maybe the information I wrote is wrong, I will revise it when I have time. Thank you for reminding me
-
+1 6.0 years ago
Opportunity and spirit actually carried the same amount of instruments
-
-





Can this be in RSS?