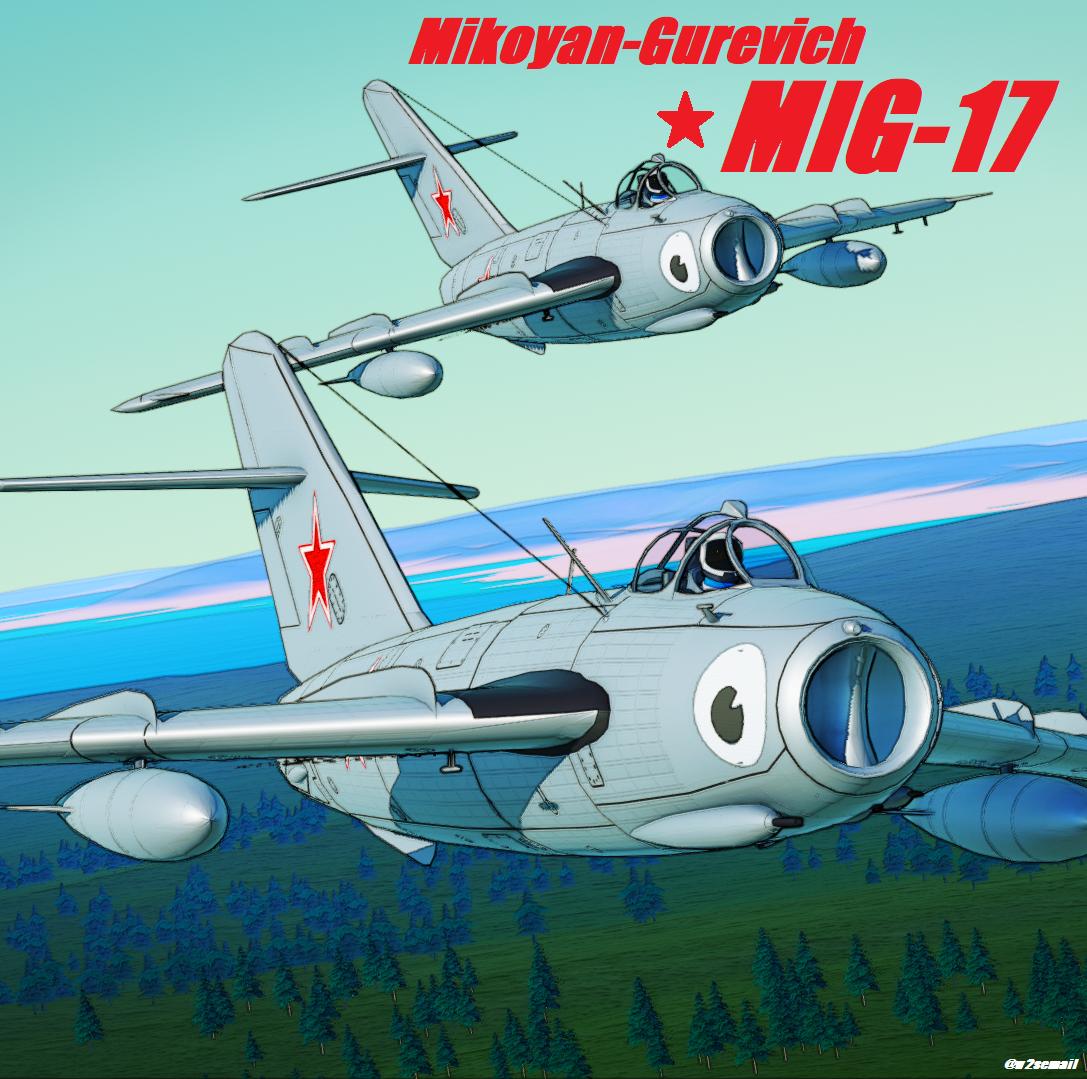
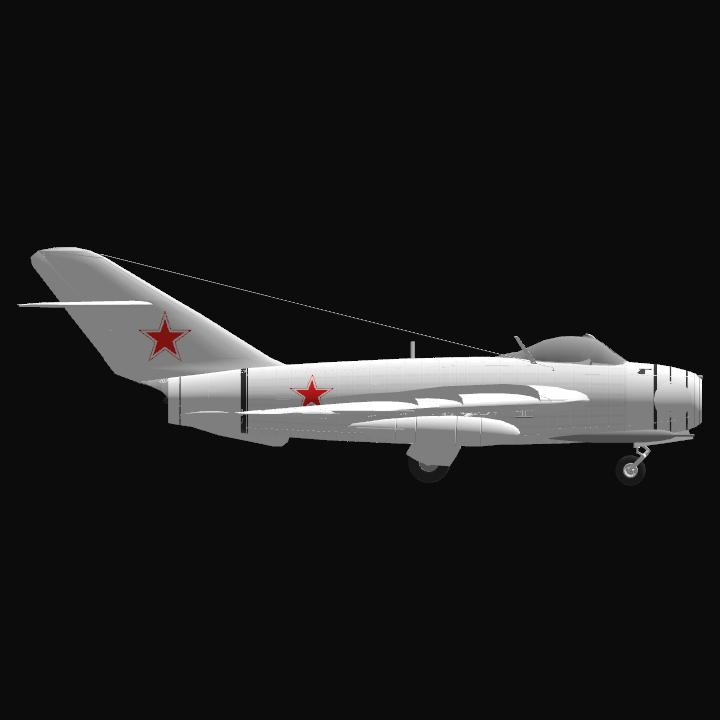
The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-17 is a high-subsonic fighter aircraft produced in the Soviet Union from 1952 and was operated by air forces internationally. The MiG-17 was license-built in China as the Shenyang J-5 and Poland as the PZL-Mielec Lim-6. The MiG-17 is still being used by the North Korean air force in the present day and has seen combat in the Middle East and Asia.
The MiG-17 was an advanced modification of the MiG-15 aircraft produced by the Soviet Union during the Korean War. Production of the MiG-17 was too late for use in that conflict and was first used in the Second Taiwan Strait Crisis in 1958. While the MiG-17 was designed to shoot down slower American bombers, it showed surprising success when used by North Vietnamese pilots to combat American fighters and fighter-bombers during the Vietnam War, nearly a decade after its initial design. This was due to the MiG-17 being more agile and maneuverable than the American F-4 Phantom and F-105 Thunderchief, which were focused on speed and long range combat, as well as the fact that MiG-17 was armed with guns, which initial models of the F-4 Phantom lacked.
While the MiG-15bis introduced swept wings to air combat over Korea, the Mikoyan-Gurevich design bureau had already begun work on its replacement in 1949 (originally the MiG-15bis45) in order to fix any problems found with the MiG-15 in combat.[2] The result was one of the most successful transonic fighters introduced before the advent of true supersonic types such as the Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-19 and North American F-100 Super Sabre. The design would ultimately still prove effective into the 1960s when pressed into subsonic dogfights over Vietnam against much faster planes that were not optimized for maneuvering in such slower speed, short-range engagements.
While the MiG-15 used a Mach sensor to deploy airbrakes because it could not safely exceed Mach 0.92, the MiG-17 was designed to be controllable at higher Mach numbers.[3] Early versions that retained the original Soviet copy of the Rolls-Royce Nene engine, the Klimov VK-1, were heavier with equal thrust. Later MiG-17s would be the first Soviet fighter application of an afterburner, which burned extra fuel in the exhaust of the basic engine to give extra thrust at a high efficiency cost.
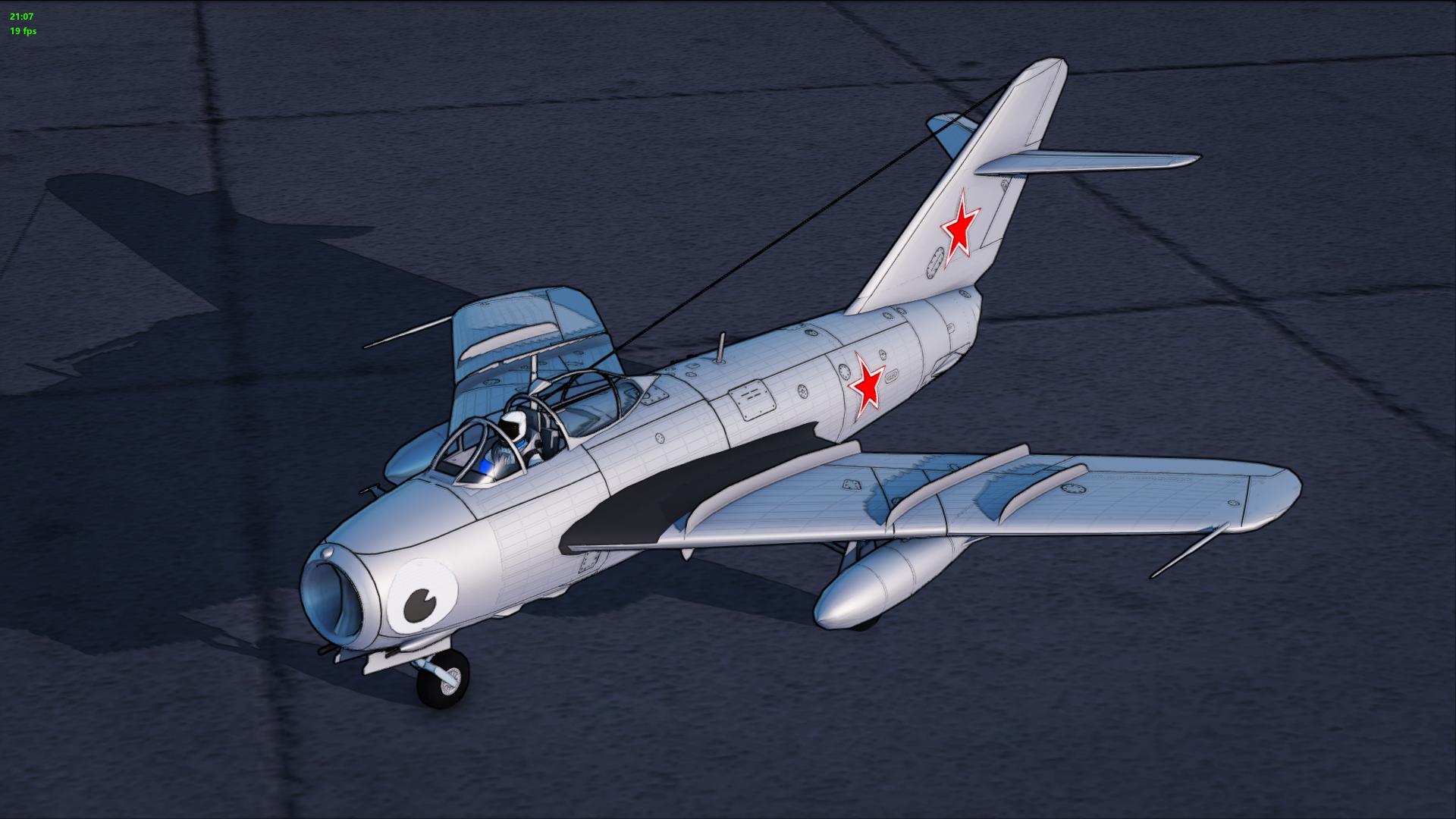
Though the MiG-17 looks very similar to the MiG-15, it had a new thinner and more highly swept wing and tailplane for speeds approaching Mach 1. While the F-86 introduced the "all-flying" tailplane, which made the aircraft more controllable near the speed of sound, this feature would not be adopted on MiG aircraft until the fully supersonic MiG-19.The wing sweep was 45° (like the U.S. F-100 Super Sabre) near the fuselage and 42° for the outboard part of the wing. The stiffer wing resisted the tendency to bend its wingtips and lose aerodynamic symmetry unexpectedly at high speeds and wing loads.
------------------------wiki
AG3-Canopy
AG2-Flap
AG1-Engine
Have a good time!










@ferreira i dont know 😥