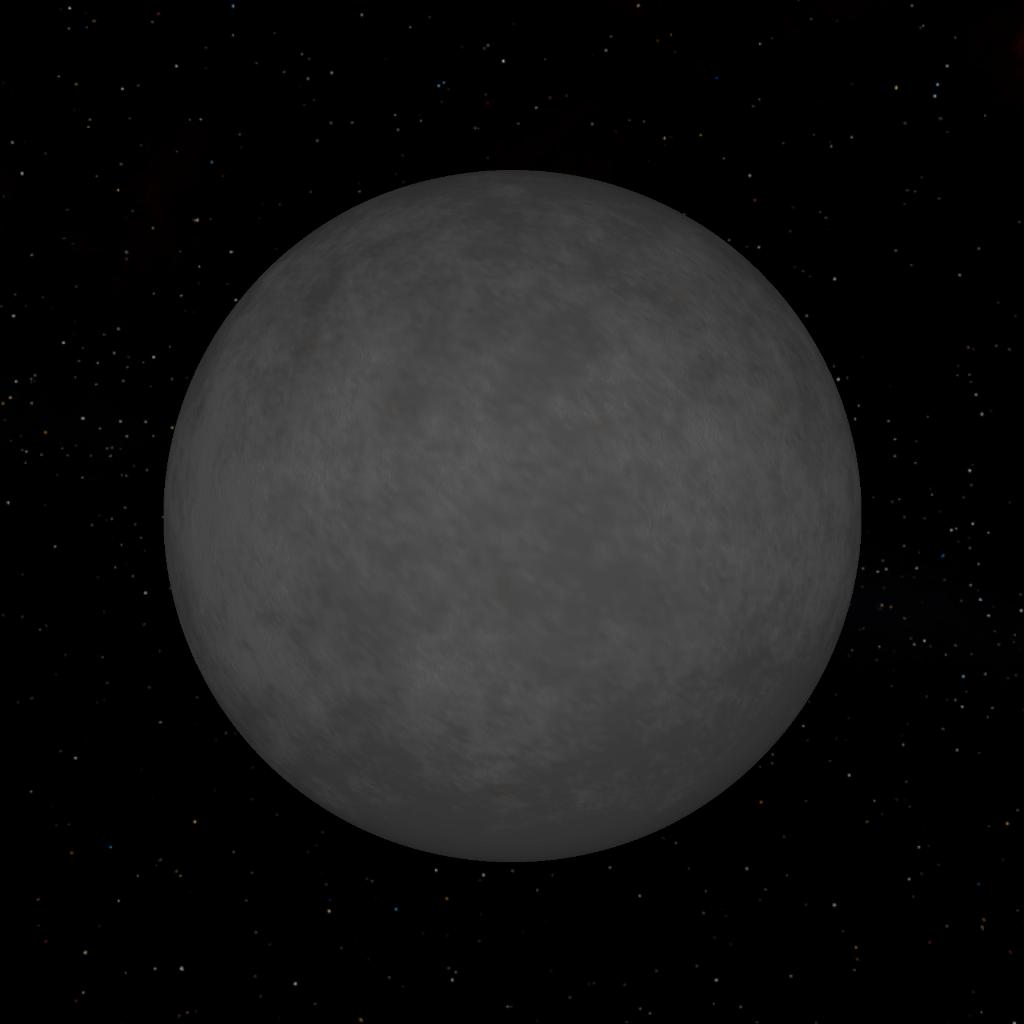
Ariel is the fourth-largest moon of Uranus. Ariel orbits and rotates in the equatorial plane of Uranus, which is almost perpendicular to the orbit of Uranus, so the moon has an extreme seasonal cycle.
It was discovered on 24 October 1851 by William Lassell and named for a character in two different pieces of literature. As of 2019, much of the detailed knowledge of Ariel derives from a single flyby of Uranus performed by the space probe Voyager 2 in 1986, which managed to image around 35% of the moon's surface. There are no active plans at present to return to study the moon in more detail, although various concepts such as a Uranus Orbiter and Probe have been proposed.
After Miranda, Ariel is the second-closest of Uranus's five major rounded satellites. Among the smallest of the Solar System's 20 known spherical moons (it ranks 14th among them in diameter), it is believed to be composed of roughly equal parts ice and rocky material. Its mass is approximately equal in magnitude to Earth's hydrosphere.
Like all of Uranus's moons, Ariel probably formed from an accretion disc that surrounded the planet shortly after its formation, and, like other large moons, it is likely differentiated, with an inner core of rock surrounded by a mantle of ice. Ariel has a complex surface consisting of extensive cratered terrain cross-cut by a system of scarps, canyons, and ridges. The surface shows signs of more recent geological activity than other Uranian moons, most likely due to tidal heating.
GENERAL INFO
- Created On: iOS
- Game Version: 1.3.204.1
CHARACTERISTICS
- Radius: 579 km
- Sea Level: None
- Surface Gravity: 0.4 m/s
- Rotational Period: 10h
- Escape Velocity: 680.5 m/s
- Mass: 2.01E+21kg
Atmosphere
- No Atmosphere
EQUIRECTANGULAR MAP